[ Stack 스택 / Queue 큐 ]
java.util.collection
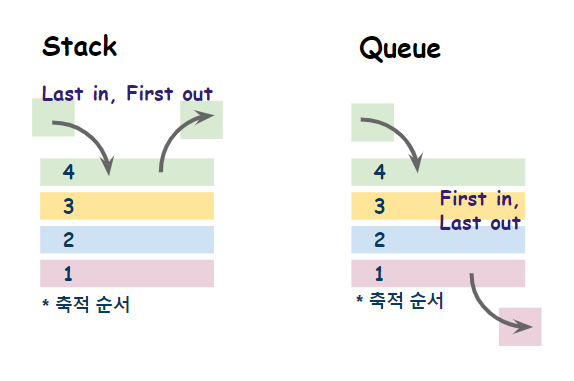
stack
: (LIFO) last-in-first-out 마지막에 추가된 요소가 먼저 추출되는 자료구조
: pop()메서드를 이용하면, 추출되며 사라짐.
stack 예제
import java.util.Stack;
public class TestStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
// 축적 메서드 : push(value)
stack.push("a");
stack.push("b");
stack.push("c");
stack.push("d");
stack.push("e");
System.out.println(stack); // [a, b, c, d, e]
// 반환 메서드 : .peak()
// 가장 마지막에 추가한 요소가 반환됨
System.out.println(stack.peek()); // e
// 추출 메서드 : .pop()
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // e
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // d
System.out.println(stack); // [a, b, c]
// 요소 유무 확인 메서드 :empty()
// 요소 있으면 False, 비어있으면 True
System.out.println(stack.empty()); //false
}
}
(message) Queue
: FIFO (first-in-first-out) 가장 먼저 추가된 요소가 먼저 추출되는 자료구조
Queue 예제
package step1;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class TestQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
// 축적 메서드 : add(value)
queue.add("안녕하세요");
queue.add("문자 보시면 답장 부탁드립니다");
queue.add("빨리 답장 주세요!");
queue.add("기한 만료되어 신청이 취소되었습니다.");
// 반환 메서드 : .peak()
// 가장 처음의 요소가 반환된다
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 안녕하세요
// 추출 메서드 : .poll()
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 안녕하세요
System.out.println(queue);
// [문자 보시면 답장 부탁드립니다, 빨리 답장 주세요!, 기한 만료되어 신청이 취소되었습니다.]
// 요소 유무 확인 메서드: isEmpty();
System.out.println(queue.isEmpty()); //false
}
}
}
[ Exception ]
java.lang.Exception
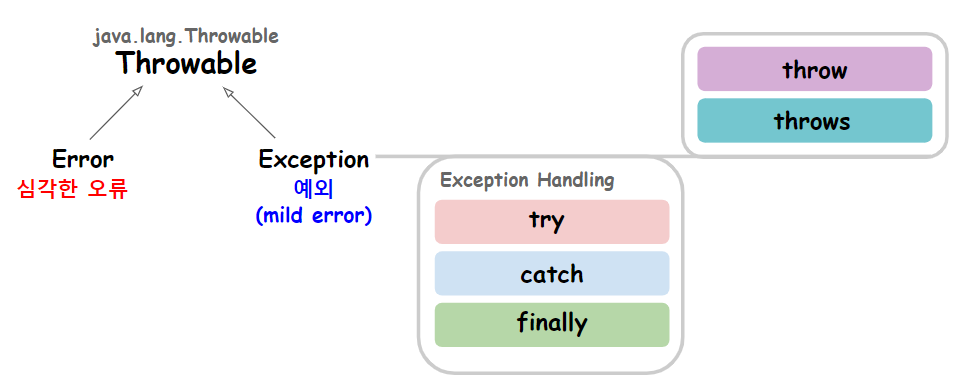
: Exception Handling (예외처리)란, 프로그램 실행 중
1. 예외상황이 발생했을 때,
2. 대안작업을 실행하고,
3. 프로그램을 정상실행하는 것을 목적으로 한다.
Exception 관련 주요 KEYWORD
- try : 예외 발생 예상 지점(블록)
- catch : 예외 처리, 예외 발생 시 대안 작업을 실행하고 프로그램은 정상 실행
- finally : 항상 실행, 예외 발생 유무 관계없이 무조건 실행 (**이름은 finally지만, firstofall의 의미를 가진다.)
- throw : 예외를 발생
- throws : (예외 발생 시) 예외를 호출한 곳으로 에러 메시지 전달
예외 처리 영역 - try / catch
예외 위임 영역 - throw / throws
try, catch, finally
> Exception이 발생하면, JVM은 예외정보 전달 후 비정상 종료한다.
예제
public class TestException1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Exception 발생하면 프로그램이 실행 중단한다
String name = "앨리스";
name = null;
System.out.println(name.length());
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 수행");
}
}error message : NullPointerException

Exception Handling(try, catch, finally) 이용한 예제
public class TestException2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Exception 발생하면 프로그램이 실행 중단한다
String name = "앨리스";
name = null;
// try : 예외 발생 지점
try
{
System.out.println(name.length());
}
// catch : 예외 발생 시 대안흐름 시행
catch (NullPointerException ne)
{
System.out.println("대안작업 실행");
}
// finally : 항상 실행
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 수행");
/*출력값:
* 대안작업 실행
* 프로그램 정상 수행
*/
}
}
> 하나의 try 블럭 안에 다양한 예외가 발생할 경우, 여러개의 catch 구문이 가능하다.
단, catch 블럭 내의 예외 발생 클래스를 자식클래스 → 부모클래스 순으로 정의해야 한다.
*catch의 Exception은 최대한 구체적으로 설정하는 것이 좋다.
여러 개의 catch문을 사용한 예제
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TestException3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
String name = "마거렛";
name = null;
// try
try
{
System.out.println(list.get(1)); //list가 비어서 error
System.out.println(name.length()); //name이 null이라 error
}
// catch
catch (NullPointerException ne)
{
System.out.println("대안작업 실행");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("대안작업 실행2");
}
// finally
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 수행");
/*출력값:
* 대안작업 실행2
* 프로그램 정상 수행
*/
}
}
* catch 첫번째 블록(대안작업 실행)이 실행이 안된 이유?
** 출금작업 단위(트랜잭션)를 예로 확인해보자.
|
try { 1. 카드삽입 --> 카드오류 Exception / 문제 발생 시, exception 발생으로 2,3,4 실행 안됨 2. 작업선택 3. 금액입력 --> 잔액부족 Exception 4. 출금 } catch (카드 오류) {} --> 카드삽입에서 오류 발생 시 실행됨 catch (금액 오류) {} --> 금액입력에서 오류 발생 시 실행됨 |
Exception 예외 발생 시, 실행의 흐름을 알아보는 예제
public class TestException4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String age = "twentyone";
try //예외 발생 지점
{
int intAge = Integer.parseInt(age);
System.out.println(intAge + 1);
System.out.println("d");
}
catch (NumberFormatException ne)
{
System.out.println("a");
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("b");
}
System.out.println("c");
/* 출력값:
* a
* c
*/
}
}
1. int intAge = Integer.parseInt(age); 에서 오류 발생 => 오류명 "NumberFormatException"
2. 오류명에 따른 catch (NumberFormatException ne) 구문으로 이동
3. catch 구문 실행 => a 출력
4. catch가 실행되었으므로 그 뒤 이어서 실행 => c 출력
finally 예제
public class TestFinally {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = null;
try
{
System.out.println(name.length()); //error : NullPointerException
System.out.println("추가작업");
}
catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ie) //error가 이거 아님 -> catch 실패
{
System.out.println("범위초과");
}
catch (NullPointerException ne) //이 단위에서 catch 수행
{
System.out.println("null이므로 실행 불가");
}
finally //error, catch 여부와 상관없이 항상 수행
{
System.out.println("finally 항상 수행");
}
// catch 성공 경우의 실행
System.out.println("정상 수행");
/* 출력값:
* null이므로 실행 불가
* finally 항상 수행
* 정상 수행
*/
}
}
throws / throw
: 프로그램이 분산되어 있을 때, 서로의 예외정보를 전달할 수 있다.
현재 class에서 발생한 에러가 아닌, 다른 class에서 error가 발생했을 경우에 사용한다.
→ error(exception)이 발생된 class에서 exception handling(try, catch, finally)을 한다.
throws → 호출한 class에 위임 (문제가 발생한 메세지를 전달)
try/catch → 본인 class에서 처리
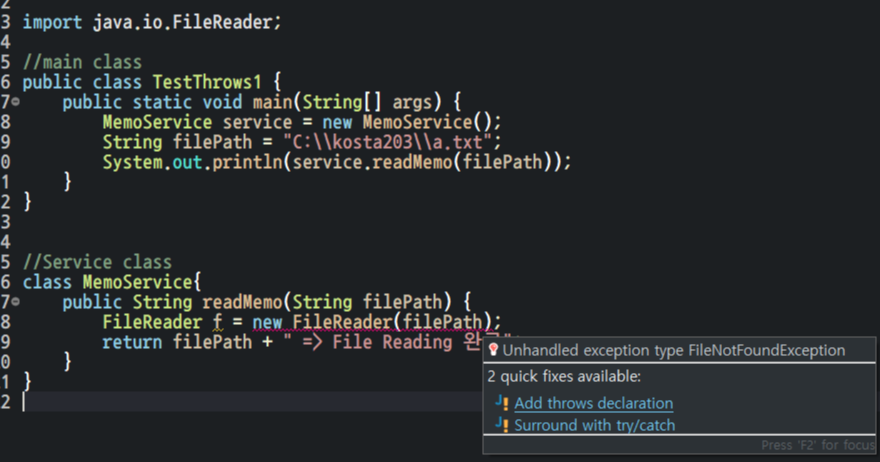
throws 를 선택한 예제
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
//main class
//오류 원인 제공 class
public class TestThrows1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MemoService service = new MemoService();
//존재하는 path => 정상 수행
String filePath = "C:\\kosta203\\a.txt";
//존재하지 않는 path
String filePath2 = "C:\\kosta203\\b.txt";
try
{
System.out.println(service.readMemo(filePath));
System.out.println(service.readMemo(filePath2));
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//Service class
//오류 발생 class
class MemoService{
public String readMemo(String filePath) throws FileNotFoundException {
FileReader f = new FileReader(filePath);
System.out.println("존재하는 파일이므로 입력 작업 수행");
return filePath + " => File Reading 완료";
}
}
MemoService(service class) → TestThrows(main class)로 error를 throws 함
TestThrows(main class) 에서 오류 메시지 출력 (FileNotFoundException 메세지: (지정된 파일을 찾을 수 없습니다))
출력 결과)

Exception관련 keyword 전체를 이용해 프로그램을 작성하고
실행결과를 예상해보는 예제 (**꼼꼼히 읽어보세요 **)
//main Class
public class TestThrows4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DateService service = new DateService();
int day = 0;
try
{
service.register(day);
//"무 조 건" finally 출력
//day가 0인 경우 : DayException 실행되어, catch블럭으로 이동
//day가 30인 경우 : pass
System.out.println("no Exception");
//day가 0인 경우 : pass
//day가 30인 경우 : 앞 try에서 exception이 발생하지 않았으므로, 실행
}
catch (DayException de)
{
System.out.println(de.getMessage());
//day가 0인 경우 : Out of Range
//day가 30인 경우 : exception이 발생하지 않았으므로, catch문 수행X
}
}
}
//Exception Class
class DayException extends Exception{
//Overloading
DayException(String message){
super(message);
}
}
// Service Class
class DateService {
public void register(int day) throws DayException {
try
{
if (day < 1 || day > 31)
throw new DayException("Out of Range");
//throw : 예외인 DayException를 발생시켜라
//new : DayException 객체를 생성해라
System.out.println("try_if");
//day가 0일 경우 : pass
//day가 30일 경우 : 실행
}
finally //예외조건 유무와 관계없이(Exception이 발생하기 전) 먼저 실행
{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}


